Supreme Tips About How To Treat Refeeding Syndrome

What it is, and how to prevent and treat it
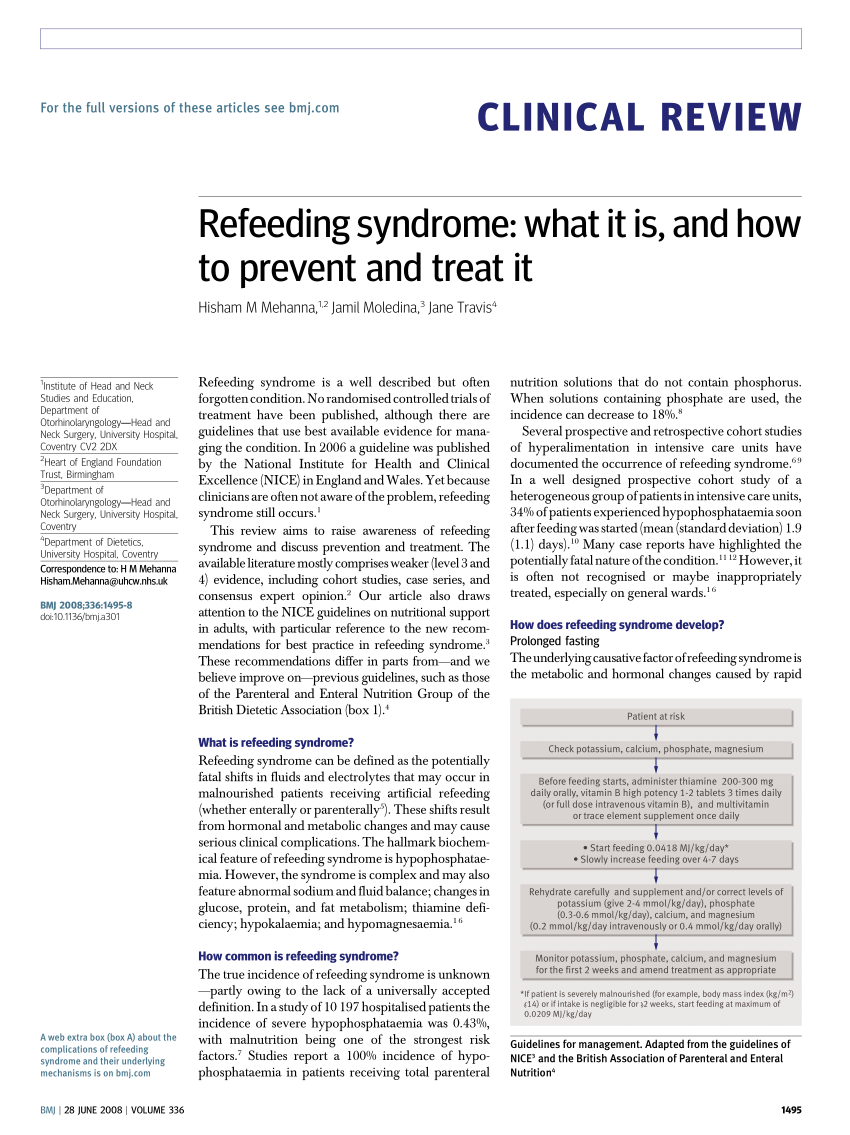
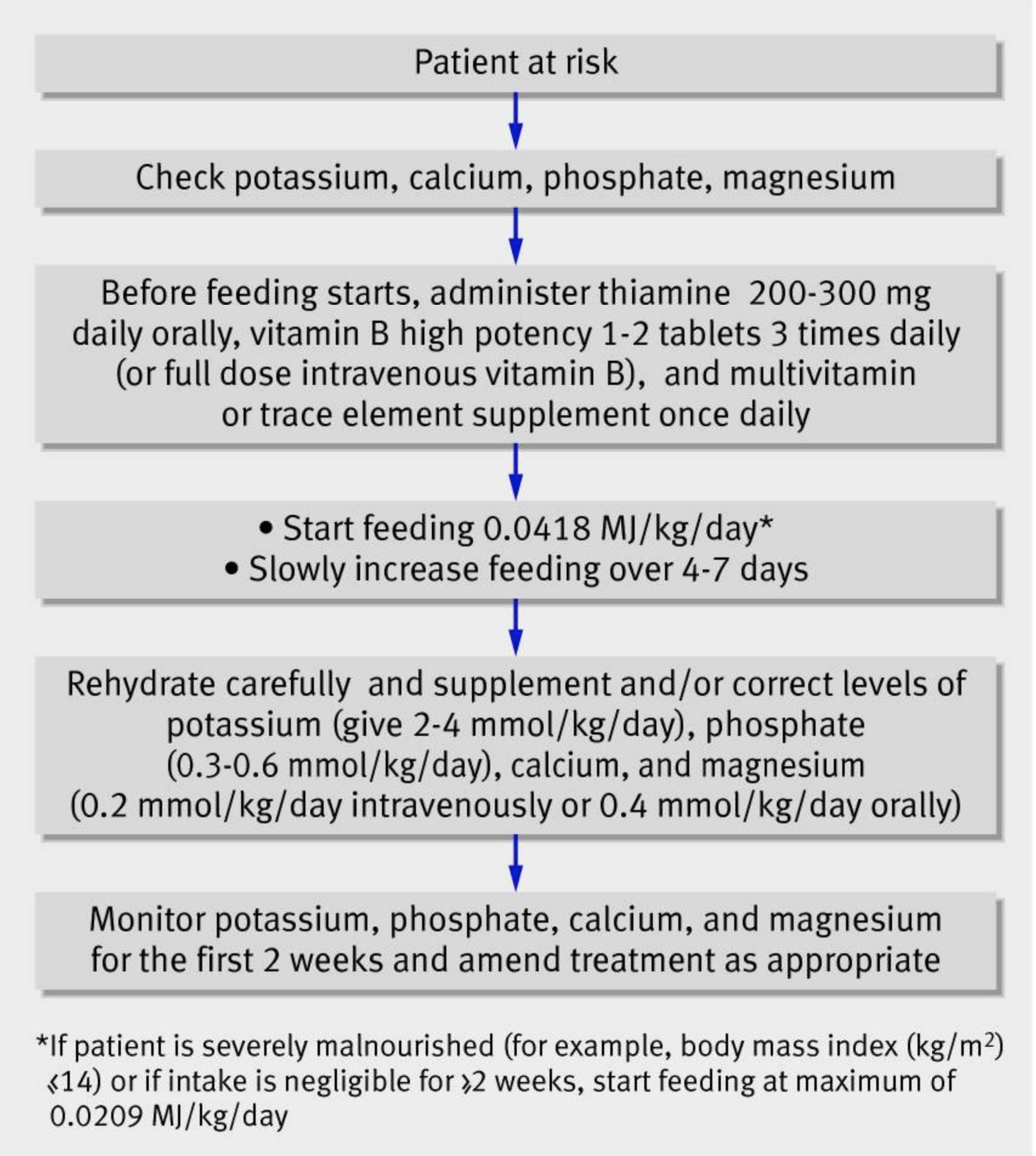
How to treat refeeding syndrome. Refeeding syndrome (rfs) is the metabolic response to the switch from starvation to a fed state in the initial phase of nutritional therapy in patients who are severely malnourished or metabolically stressed due to severe illness. Refeeding syndrome = a group of clinical findings that occur in severely malnourished individuals undergoing nutritional support. Management of a patient at risk of refeeding:
Occurs in the setting of prolonged starvation followed by provision of nutritional supplementation from. The web page provides rapid reference, epidemiology, signs and symptoms, prevention. Certain conditions may increase your risk for this.
It occurs due to electrolyte depletion and thiamine deficiency. Treatment recovery prevention outlook refeeding syndrome is caused by sudden shifts in the electrolytes that help your body metabolize food. What are the clinical features?
If the patient has one or more of the following: You can develop loss of body. Rfs derives from an abnormal electrolyte and fluid shifts leading to.
Refeeding syndrome is a complication of treatment for malnutrition. Refeeding syndrome is a serious complication of severe malnutrition or eating disorders that occurs when calories are provided to an individual who has been undernourished. Refeeding syndrome is detected by considering the possibility of its existence and by using the simple biochemical investigations described above.
Bmi 10% in 6 months. Abstract refeeding problems have been recognised since the the liberation of starved communities under siege. Adherence to the nice guidelines for preventing and treating refeeding syndrome (boxes 2 and 3) should reduce the incidence and associated complications of the syndrome.
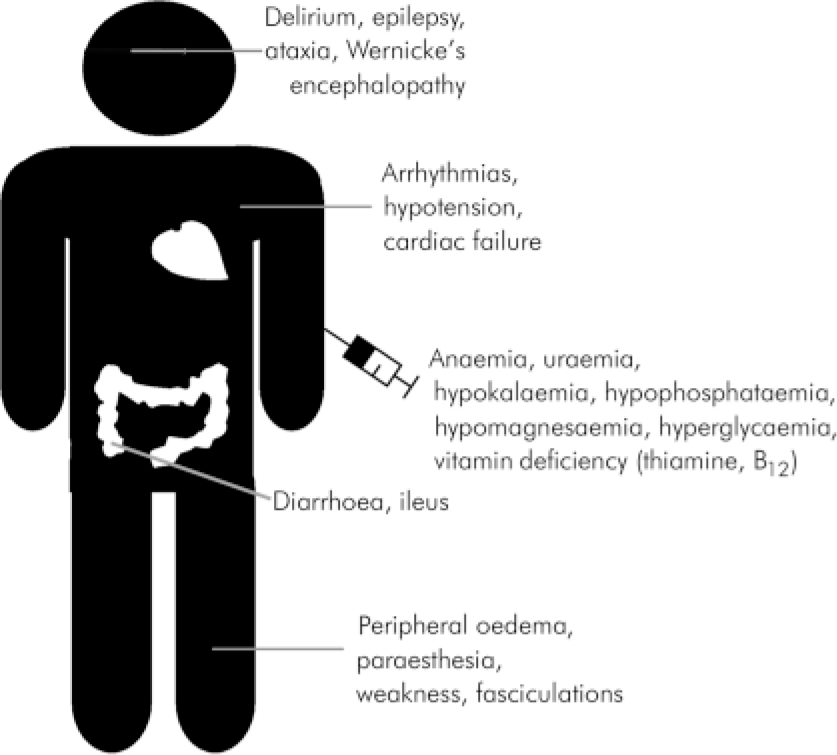
Abstract the refeeding syndrome (rfs) is a potentially serious, but still overlooked condition, occurring in individuals who are rapidly fed after a period of severe undernourishment. Depending on the underlying cause of malnutrition, other interventions may be needed, such as a treatment for a bowel problem. The main clinical problems may relate to hypophosphataemia, hypomagnesaemia and hypokalaemia with a risk of sudden death;.
If the syndrome is detected, the rate of. It’s essential to replace lost nutrients because malnutrition has serious health consequences. Little or no nutritional intake.
Refeeding syndrome is a potentially fatal complication of refeeding after underfeeding for a long time. All patients monitor u&e, mg, ca and po4 prior to feeding and daily until stable. Bringing someone with an eating disorder back to a healthy weight can resolve structural changes to the heart caused by malnutrition, but it must be done cautiously, mehler said.
How can refeeding syndrome be detected and treated? Treatment may also be need if refeeding syndrome causes any complications, such as heart failure, insulin to control. It can cause electrolyte imbalances, organ dysfunction and death.
![(PDF) [Refeeding Syndrome A Review of the Literature.]](https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/262930869_Refeeding_Syndrome_A_Review_of_the_Literature/links/5575cd1708aeb6d8c01ae52e/largepreview.png)